

Due to the way it is produced, CSF has a higher chloride level than plasma, and an equivalent sodium level.
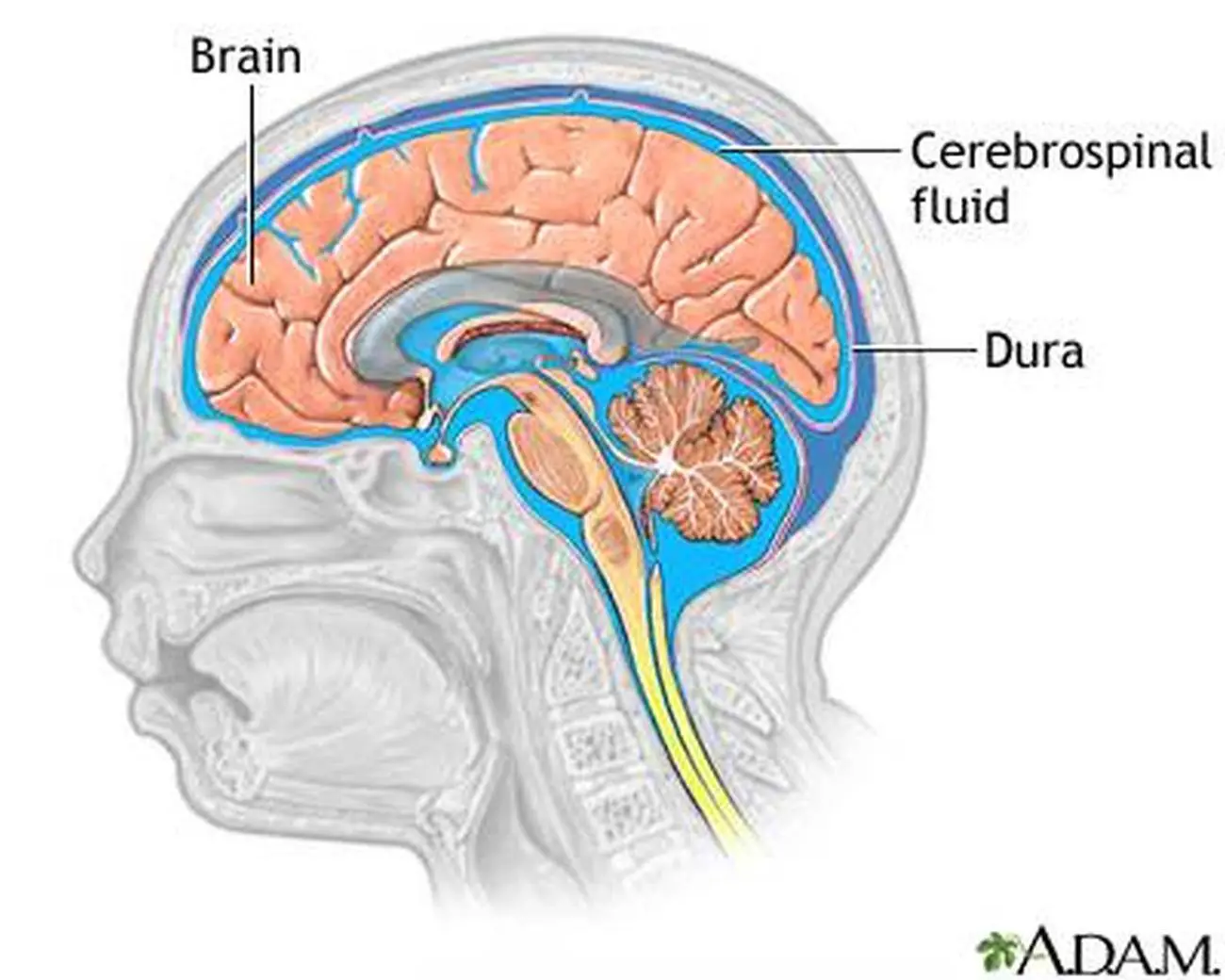
Contents ĬSF is derived from blood plasma and is largely similar to it, except that CSF is nearly protein-free compared with plasma and has some different electrolyte levels. Some authors dispute this, posing that there is no unidirectional CSF circulation, but cardiac cycle-dependent bi-directional systolic-diastolic to-and-from cranio-spinal CSF movements. Fluid movement is pulsatile, matching the pressure waves generated in blood vessels by the beating of the heart. ĬSF moves in a single outward direction from the ventricles, but multidirectionally in the subarachnoid space. There is a connection from the subarachnoid space to the bony labyrinth of the inner ear making the cerebrospinal fluid continuous with the perilymph in 93% of people. CSF is present within the subarachnoid space, which covers the brain, spinal cord, and stretches below the end of the spinal cord to the sacrum. From the fourth ventricle, the fluid passes into the subarachnoid space through four openings – the central canal of the spinal cord, the median aperture, and the two lateral apertures. From here, CSF passes through the interventricular foramina to the third ventricle, then the cerebral aqueduct to the fourth ventricle. The majority of CSF is produced from within the two lateral ventricles.
#BRAIN FLUID SERIES#
The ventricles are a series of cavities filled with CSF. This CSF circulates within the ventricular system of the brain. There is about 125–150 mL of CSF at any one time. In 1914, Harvey Cushing demonstrated that CSF is secreted by the choroid plexus. This can be used to test the intracranial pressure, as well as indicate diseases including infections of the brain or the surrounding meninges.Īlthough noted by Hippocrates, it was forgotten for centuries, though later was described in the 18th century by Emanuel Swedenborg. The ependymal cells of the choroid plexus have multiple motile cilia on their apical surfaces that beat to move the CSF through the ventricles.Ī sample of CSF can be taken from around the spinal cord via lumbar puncture. There is also a connection from the subarachnoid space to the bony labyrinth of the inner ear via the perilymphatic duct where the perilymph is continuous with the cerebrospinal fluid. It fills the ventricles of the brain, cisterns, and sulci, as well as the central canal of the spinal cord. CSF also serves a vital function in the cerebral autoregulation of cerebral blood flow.ĬSF occupies the subarachnoid space (between the arachnoid mater and the pia mater) and the ventricular system around and inside the brain and spinal cord. CSF acts as a shock absorber, cushion or buffer, providing basic mechanical and immunological protection to the brain inside the skull. There is about 125 mL of CSF at any one time, and about 500 mL is generated every day. Cerebrospinal fluid ( CSF) is a clear, colorless body fluid found within the tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord of all vertebrates.ĬSF is produced by specialised ependymal cells in the choroid plexus of the ventricles of the brain, and absorbed in the arachnoid granulations.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
